RedisLabs Enterprise Cluster Nodes IP management
RedisLabs Enterprise Cluster (RLEC1) nodes can split network traffic in two categories: internal using one and only one network interface to communicate between nodes for replication and cluster management, and external using one or more interfaces for application connections. Here is how to change these settings after initial setup, using the REST API or the commandline tools.
You can find links to the related video recordings and printable materials at the end of this post.
Prerequisites
You have a RedisLabs Enterprise Cluster up and running. Either you added/removed network interfaces to the nodes or you changed the IP addresses of the network interfaces.
Why
When you create a database in RLEC, it gives you an “endpoint”. this is the database name that is used by the applications to connect to the database. In RLEC, every node execute the same processes, including a proxy process to handle client connections.
Depending on your database endpoint proxy policy, one of them or several of them will be configured to handle connections for this database. This means that your client can connect to the database using any of these configured proxies and need to know which of them are configured. This can be achieved using a DNS resolution, or a discovery service.
Whatever the protocol used is, it needs to return the relevant list of IP addresses, ie the list of external IP addresses of the relevant nodes, but not the internal IP addresses.
Maybe you made a mistake during the initial setup, or you changed your hardware configuration to add or remove network interfaces, or you want to optimize your network usage, or … Anyway, you need to change the external addresses list for some of your nodes.
Despite you can check the internal and external addresses from the web administration interface, under the “Nodes” menu, in a specific node’s “Configuration” tab, you can not change them here.
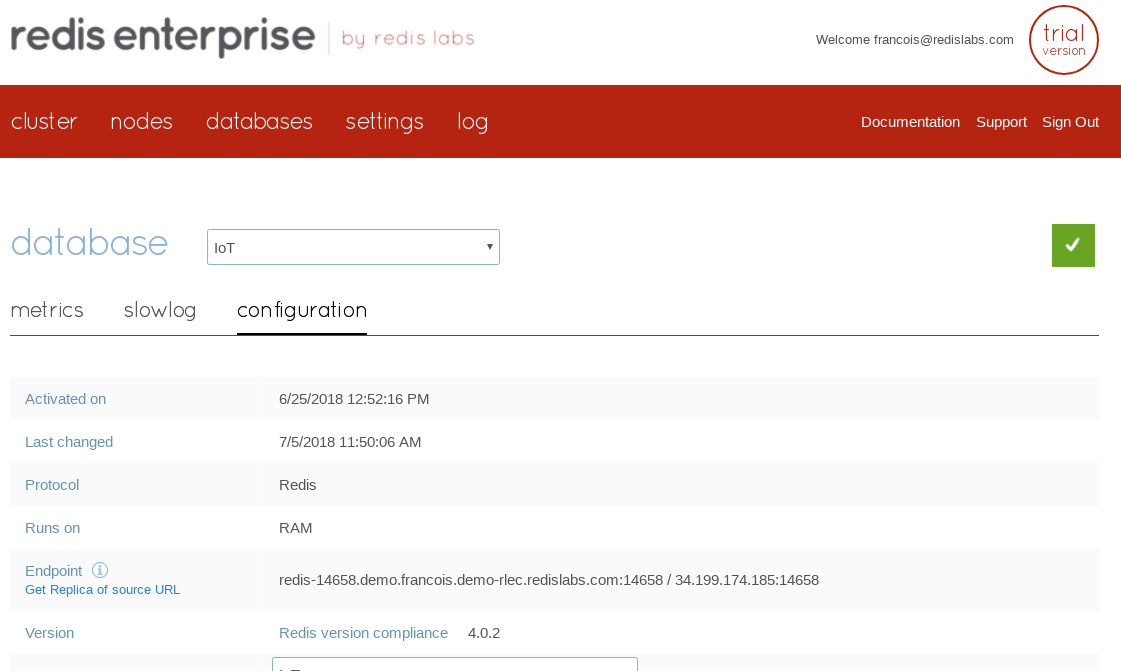
You can change these settings using either the “rladmin” commandline tool or the REST API calls.
This can be useful when you provisionned a node quickly. By default, all the network interfaces are in the external list, the endpoints will return all the addresses, but some of them might not be reachable by your client applications
With rladmin
You can open a terminal window on any of the cluster nodes and login using a “redislabs” group member to use rladmin. Then, you can either start it interactively, with a comand prompt or ask it to execute a single specific command passed in arguments. The two following are strictly similar.
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# rladmin status endpoints
ENDPOINTS:
DB:ID NAME ID NODE ROLE SSL
db:1 IoT endpoint:1:1 node:3 single No
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# rladmin
RedisLabs Admin CLI
Version 5.0.2-15
Use <?> for help at any time, <TAB> for command completion.
rladmin> status endpoints
ENDPOINTS:
DB:ID NAME ID NODE ROLE SSL
db:1 IoT endpoint:1:1 node:3 single No
rladmin> quit
The first one is handy for scripting and batching commands, the second one for interactive administration with auto-completion.
Check the external addresses
You can either request the configuration for all the nodes or you can specify one specific node to get the external addresses :
rladmin> info node 1
node:1
address: 172.31.56.5
external addresses: 34.199.174.185
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
rladmin> info node
node:1
address: 172.31.56.5
external addresses: 34.199.174.185
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
node:2
address: 172.31.55.7
external addresses: 34.199.175.137
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
node:3
address: 172.31.50.67
external addresses: 34.195.100.46
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
If I try to resolve one of my endpoints, I get only one IP address :
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# nslookup redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Server: 172.31.0.2
Address: 172.31.0.2#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Address: 34.195.100.46
This endpoint is configured to have only one proxy listening, this proxy is currently located on the third node and the third node has only one external address.
Add an address to a node’s external addresses list
Now that you have the list of your nodes and the related external addresses list, you can add an address to the external addresses list of a node using the following command. Let’s say that I want to handle incoming client connection on both interfaces, on node 3, I need to add the 172.31.50.67 address (currently only used for internal traffic) to the external list:
rladmin> node 3 external_addr add 172.31.50.67
Updated successfully.
Then, I can check using the info node 3 command described earlier:
rladmin> info node 3
node:3
address: 172.31.50.67
external addresses: 34.195.100.46, 172.31.50.67
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
If I request a resolution for the endpoint that is currently attached to the third node’s proxy, I can see the 2 external addresses.
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# nslookup redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Server: 172.31.0.2
Address: 172.31.0.2#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Address: 34.195.100.46
Name: redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Address: 172.31.50.67
My clients will have the choice to connect.
Remove an address from a node’s external addresses list
Removing an address from an external addresses list is done with the “remove” sub-sub-command:
rladmin> info node 3
node:3
address: 172.31.50.67
external addresses: 34.195.100.46, 172.31.50.67
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
rladmin> node 3 external_addr remove 172.31.50.67
Updated successfully.
rladmin> info node 3
node:3
address: 172.31.50.67
external addresses: 34.195.100.46
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
With the REST API
The REST API documentation is included and installed when you provision a node,
alongside with the software. Here is how to use the curl command line tool.
By default, it is listening from all the nodes on port 9443, using SSL
certificates. By default, the SSL certificate are created when you bootstrapped
your cluster and are self-signed. Curl will not accept them unless you add the
“insecure” argument. So, the curl command should start with: curl
"https://localhost:9443/v1/nodes/1" --insecure
Given than you can connect from the network, you need to provide a Redis Cluster
admin credentials: -u "francois@redislabs.com:secret"
The REST API expect incoming commands and data to be formated in JSON, curl can
tell the REST API that we send JSON: -H "Content-Type:application/json" and
that we also expect the answers to be formatted in JSON: -H
"Accept:application/json"
Thus, the curl commands will start with:
curl "https://localhost:9443/v1/nodes/1" \
--insecure \
-u "francois@redislabs.com:password" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
Let’s start with this initial configuration:
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# rladmin info node
node:1
address: 172.31.56.5
external addresses: 34.199.174.185
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
node:2
address: 172.31.55.7
external addresses: 34.199.175.137
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
node:3
address: 172.31.50.67
external addresses: 34.195.100.46
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
Check the external addresses
You can either request the configuration for all the nodes or you can specify one specific node to get the external addresses :
For the first node:
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# curl "https://localhost:9443/v1/nodes/1" \
--insecure \
-X "GET" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-u "francois@redislabs.com:password"
{
"accept_servers": true,
"addr": "172.31.56.5",
"architecture": "x86_64",
"bigredis_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/flash",
"bigstore_driver": "rocksdb",
"bigstore_size": 26279878656,
"cores": 36,
"ephemeral_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/tmp",
"ephemeral_storage_size": 26279878656.0,
"external_addr": [
"34.199.174.185"
],
"os_version": "Ubuntu 16.04.3 LTS",
"persistent_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/persist",
"persistent_storage_size": 26279878656.0,
"rack_id": "",
"shard_count": 0,
"shard_list": [],
"software_version": "5.0.2-15",
"status": "active",
"supported_database_versions": [
{
"db_type": "memcached",
"version": "1.4.17"
},
{
"db_type": "redis",
"version": "3.2.11"
},
{
"db_type": "redis",
"version": "4.0.2"
}
],
"total_memory": 63314849792,
"uid": 1,
"uptime": 3633
}
For all nodes:
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# curl "https://localhost:9443/v1/nodes" \
--insecure \
-X "GET" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-u "francois@redislabs.com:password"
If I try to resolve one of my endpoints, I get only one IP address :
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# nslookup redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Server: 172.31.0.2
Address: 172.31.0.2#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Address: 34.195.100.46
This endpoint is configured to have only one proxy listening, this proxy is currently located on the third node and the third node has only one external address.
Add an address to a node’s external addresses list
Now that you have the list of your nodes and the related external addresses list, you can add an address to the external addresses list of a node using the following command. Let’s say that I want to handle incoming client connection on both interfaces, on node 3, I need to add the 172.31.50.67 address (currently only used for internal traffic) to the external list.
When using the REST API, you need to specify the whole external addresses list, you can not add or remove a single address.
curl "https://localhost:9443/v1/nodes/3" \
--insecure \
-X "PUT" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-u "francois@redislabs.com:password" \
-d '{
"external_addr": ["34.195.100.46","172.31.50.67"]
}'
Then, I can check using the info node 3 command described earlier:
rladmin> info node 3
node:3
address: 172.31.50.67
external addresses: 34.195.100.46, 172.31.50.67
recovery path: N/A
quorum only: disabled
If I request a resolution for the endpoint that is currently attached to the third node’s proxy, I can see the 2 external addresses.
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# nslookup redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Server: 172.31.0.2
Address: 172.31.0.2#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Address: 34.195.100.46
Name: redis-14658.demo.francois.demo-rlec.redislabs.com
Address: 172.31.50.67
My clients will have the choice to connect.
Remove an address from a node’s external addresses list
With the REST API, you have to specify the whole external addresses list. The first step is to get the list :
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# curl "https://localhost:9443/v1/nodes/3" \
--insecure \
-X "GET" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-u "francois@redislabs.com:password"
{
"accept_servers": true,
"addr": "172.31.50.67",
"architecture": "x86_64",
"bigredis_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/flash",
"bigstore_driver": "rocksdb",
"bigstore_size": 26279878656,
"cores": 36,
"ephemeral_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/tmp",
"ephemeral_storage_size": 26279878656.0,
"external_addr": [
"34.195.100.46",
"172.31.50.67"
],
"os_version": "Ubuntu 16.04.3 LTS",
"persistent_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/persist",
"persistent_storage_size": 26279878656.0,
"rack_id": "",
"shard_count": 2,
"shard_list": [
1,
3
],
"software_version": "5.0.2-15",
"status": "active",
"supported_database_versions": [
{
"db_type": "memcached",
"version": "1.4.17"
},
{
"db_type": "redis",
"version": "3.2.11"
},
{
"db_type": "redis",
"version": "4.0.2"
}
],
"total_memory": 63314849792,
"uid": 3,
"uptime": 5533
}
Then, you can update the whole external addresses list of node 3, without the address to remove:
curl "https://localhost:9443/v1/nodes/3" \
--insecure \
-X "PUT" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-u "francois@redislabs.com:password" \
-d '{
"external_addr": ["34.195.100.46"]
}'
Then, I can check using the command described earlier:
root@ip-172-31-56-5:~# curl "https://localhost:9443/v1/nodes/3" \
--insecure \
-X "GET" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-u "francois@redislabs.com:password"
{
"accept_servers": true,
"addr": "172.31.50.67",
"architecture": "x86_64",
"bigredis_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/flash",
"bigstore_driver": "rocksdb",
"bigstore_size": 26279878656,
"cores": 36,
"ephemeral_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/tmp",
"ephemeral_storage_size": 26279878656.0,
"external_addr": [
"34.195.100.46"
],
"os_version": "Ubuntu 16.04.3 LTS",
"persistent_storage_path": "/var/opt/redislabs/persist",
"persistent_storage_size": 26279878656.0,
"rack_id": "",
"shard_count": 2,
"shard_list": [
1,
3
],
"software_version": "5.0.2-15",
"status": "active",
"supported_database_versions": [
{
"db_type": "memcached",
"version": "1.4.17"
},
{
"db_type": "redis",
"version": "3.2.11"
},
{
"db_type": "redis",
"version": "4.0.2"
}
],
"total_memory": 63314849792,
"uid": 3,
"uptime": 5846
}
Materials and Links
| Link | Description |
|---|---|
| RedisLabs.com | The company behind Redis |
| Redis.io | Redis project home page |
| [Video] | Demonstration screencast recording |
Footnotes
-
RLEC, RedisLabs Enterprise Cluster, is now known as Redis^e for Redis Enterprise. ↩